Download NATO’s broadcast-quality video content free of charge

Log in
NATO MULTIMEDIA ACCOUNT
Access NATO’s broadcast-quality video content free of charge

Check your inbox and enter verification code
You have successfully created your account
From now on you can download videos from our website
Subscribe to our newsletter
If you would also like to subscribe to the newsletter and receive our latest updates, click on the button below.
Enter the email address you registered with and we will send you a code to reset your password.
Didn't receive a code? Send new Code
The password must be at least 12 characters long, no spaces, include upper/lowercase letters, numbers and symbols.
Your password has been updated
Click the button to return to the page you were on and log in with your new password.
Endorsed by Allied Heads of State and Government on 25 June 2025
Executive summary
Already today, new technological products can help to address critical capability shortfalls, improve interoperability and enhance the effectiveness of existing and future platforms. These new technological products are increasingly being developed by non- traditional suppliers, with new approaches to product development, such as technology-focused companies, medium sized enterprises and start-ups such as those the Alliance supports through its Defence Innovation Accelerator for the North Atlantic (DIANA) and the NATO Innovation Fund (NIF). However, more must be done to bring these cutting-edge technologies into the hands of Allied operators to strengthen the Alliance’s deterrence and defence posture.
This Rapid Adoption Action Plan, including its political commitment and pilots, aims to significantly accelerate the pace at which the Alliance adopts new technological products, in general to within a maximum of 24 months. It provides Allies with shared objectives and best practices, underpinned by NATO support, to:
- Accelerate procurement and integration: Allies will procure new technological products at greater speed, sharing market research on a voluntary basis, and best practices, and accelerating their adoption by introducing agility, flexibility and expertise – as well as a mindset embracing more acquisition and procedural risks – into the relevant national processes and structures.
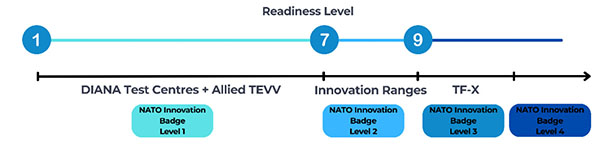
- De-risk new technological products: The Alliance will enable continuous, iterative co-development and testing to battle-ready technological products in support of NATO capability priorities. To this end, NATO and Allies will leverage, for example, DIANA to enhance testing of innovative technologies, develop new Innovation Ranges to further test promising products and pilot NATO Task Force Xs to help integrate mature technological products into the Allied force mix. With ‘NATO Innovation Badges’ being awarded, the Alliance will build trust in tested products as they mature.
- Ensure that new technological products are better tailored to Allied military needs: The Alliance will communicate demand signals and priorities derived from NATO’s Defence Planning Process (NDPP) to Allied innovation ecosystems and establish a NATO Front Door for Industry to communicate collaboration opportunities and priorities to industries.
Vision
- To win the technology adoption race, which is critical to strengthen the Alliance’s deterrence and defence posture today and in the future, the Alliance has to operate at pace. The Alliance has the most robust innovation ecosystem in the world, with top class start-ups, scale-ups, defence contractors, universities and researchers, and substantial investment capital. In the current challenging security environment, Allied armed forces urgently need the most innovative and effective technologies and products.
- With this plan, Allies and NATO will embrace a new mindset and a better approach to defence innovation – embracing more risk at early stages to achieve better results, faster. Allies will accelerate substantially the pace of adoption of innovative solutions into Allied armed forces, as an essential part of their overall accelerating modernisation, and strengthen collaboration with defence innovation ecosystems across the Alliance.
- Through this Rapid Adoption Action Plan, Allies will take decisive steps to find and foster the best technologies in the Alliance, test, and be able to adopt them at the speed of relevance, in most cases within 24 months. In support of the Defence Investment Pledge, Allies will dedicate adequate resources for flexible, rapid adoption of new technological products, in accordance with national budgetary processes.
The Technology Adoption Challenge
- The adoption of new technological products and services, at the speed of relevance, leveraging Emerging and Disruptive Technologies (EDT) and other relevant technologies, with dual-use or solely military applications, is fundamental to maintain the Alliance’s technological edge, which is an essential enabler of our military dominance and the viability of our deterrence and defence posture.
- The speed at which new technological products are being developed outpaces the Alliance’s ability to procure and integrate them, and evolve the relevant doctrine. At the same time, the Alliance’s technological edge is narrowing as our strategic competitors and potential adversaries rival the Alliance’s ability to adopt EDT solutions into our militaries.
- New technological products can already today address critical capability shortfalls, improve interoperability and enhance the effectiveness of existing and future platforms. These are developed by traditional defence firms and non-traditional suppliers1. Across Allied Innovation Ecosystems, non-traditional suppliers in the private sector in particular have become increasingly critical drivers of new technological products. Their business models fundamentally diverge from established approaches in defence industries, requiring adaptions from both system integrators and governments if they are to acquire the solutions these suppliers can offer.
- The Alliance has successfully bolstered its capacity to promote the development of new technological products and to engage with Allied defence innovation ecosystems, including through the operationalisation of the Defence Innovation Accelerator for the North Atlantic (DIANA) and the NATO Innovation Fund (NIF).
Objective & Aims
- The objective of this Action Plan is to enhance substantially the Allies’ and NATO’s speed of adoption of new technological products in general within 24 months2 from identification of a need to the acquisition and integration of a new technological product into Allied armed forces, leveraging NATO fora, procedures and mechanisms, where possible. These products will enable Allies to meet identified NATO Defence Planning Process (NDPP) priorities, in support of the Alliance’s deterrence and defence posture.
- In support of this objective and the 24 months timeline, Allies will accelerate contracting and acquisition of new technological products, and mainstream rapid adoption efforts across the Alliance, aiming to complete incremental Testing, Evaluation, Verification and Validation (TEVV) and integration activities in general within 12 months after having identified potential solutions, and reducing the time needed for market research to in general 3 months.
Implementation principles
- The operationalisation of the Action Plan will align the Alliance’s innovation agenda with the NDPP capability targets, be driven by Allies and incentivise more flexibility in acquisition, including more acceptance of some acquisition and procedural risks.
NDPP Capability Targets-driven
- The NDPP drives transformation of the Alliance’s forces over time. New technological products offer substantial opportunities for Allies to acquire required effects, as identified in the NDPP. This Action Plan gears the Alliance’s innovation agenda to support Allied defence planning and capability development.
Allied-driven
- As capability development is almost entirely carried out nationally by Allies, this Action Plan focuses on Allies: it provides Allies with recommendations, best practices and shared objectives to accelerate the adoption of new technological products and promote interoperability. The implementation thereof will be the responsibility of Allies and could have financial and procedural implications for Allies, in accordance with national and other relevant norms. NATO has a range of fora, procedures and mechanisms which can further inform, guide, facilitate and support Allied adoption of new technological products.
- Through the implementation of this Action Plan, Allies will increasingly cooperate with, and support one another to accelerate adoption3.
Embracing risk
- To adopt new technological products and services at the speed of relevance, Allies recognise that some acquisition and procedural risks need to be an inherent part of innovation and rapid adoption processes to iterate, fail fast and reward agility and flexibility. This change in mindset requires political endorsement, policy review, appropriate incentive structures and support throughout hierarchies. The adoption of new technological products will be implemented in accordance with NATO’s values, norms, international law, and NATO’s Principles of Responsible Use.
Deliverables
- In order for the Alliance to rapidly adopt new technological products, this Action Plan identifies goals and enablers for Allies and NATO to accelerate the procurement and integration of new technological products, de-risk them, and drive targeted innovation ecosystem engagement.
A. Accelerating adoption through agile procurement and integration
Goals
- Allies should be able to acquire and begin integration of new technological products into Allied armed forces in general within 24 months. To facilitate the participation of non-traditional suppliers in capability development, Allies and NATO will embrace, where appropriate, iterative problem-based procurement, moving away from traditional requirements-based waterfall approaches, and address contractual barriers that exclude non-traditional suppliers from government contracts, in accordance with national prerogatives and other relevant norms, including security considerations.
Allies will endeavour, where possible, to create dedicated financing tools to accelerate adoption.
- In support of the Defence Investment Pledge, Allies will dedicate adequate resources for flexible, rapid adoption of new technological products, in accordance with national budgetary processes.
Enablers
A1. Allied Innovation Procurement Forum
- NATO will establish the Innovation Procurement Forum, bringing together on a regular basis relevant Allied innovation procurement experts to exchange best practices to rapidly adopt new technological products.
A2. Innovation Support Partnership
- Multinational acquisition of new technological products and dedicated contractual authorities will enhance synergies between Allies and provide quicker access to new technological products from across the Alliance.
- This Partnership should allow Allies, on a voluntary basis, to jointly and directly procure new technological products that have been competitively selected by Defence Innovation Entities of participating Allies without the need to compete again.
A3. Rapid Adoption Training
- Procurement officials, defence planners and decision makers play a critical role in enabling the rapid adoption of new technological products. To support them, NATO will develop and provide training courses for relevant Allied and NATO personnel:
- A training course for procurement and acquisition experts to promote rapid adoption best practices; and
- A defence innovation training course for decision makers and defence planners.
A4. Doctrine Development
- To accelerate the integration of new technological products into Allied Armed Forces, the Alliance will have to ensure that concept and doctrine development occurs at a commensurate pace. This needs to be anchored in a deliberate approach to transform the Alliances’ forces.
B. De-risking new technological products
Goals
- To de-risk the adoption of new technological products at the speed of relevance, Allies should be able to complete incremental TEVV and integration activities in general within 12 months after having identified potential solutions. In support of this, Allies, and NATO where possible, endeavour to:
- Make integration and TEVV environments readily available to test new technological products in different environments and real-world conditions, including in exercises. To facilitate the participation of non-traditional suppliers, Allies should consider providing funding and establishing such experimentation environments also at a non-classified level.
- Foster the pull-through of promising solutions from experimentation into capability development using appropriate procurement pathways.
- Accelerate, on a voluntary basis, cross-recognition of certification standards, including for new technological products.
Enablers
B1. NATO Innovation Badges
- To foster a coherent risk assurance framework across the Alliance, NATO Innovation Badges will be awarded to new technological products that have successfully undergone activities for example in DIANA’s network of Test Centres or Allies’ test centres, OPEX, LIVEX and/or NATO Task Force X to demonstrate their level of maturity and readiness.
- The NATO Innovation Badges will allow Allies to swiftly find new technological products that have been tested, security vetted, and de-risked at different maturity levels, creating efficiencies, and provide suppliers with a seal of approval, which will increase their credibility when engaging with operators, system integrators as well as investors.
B2. NATO Innovation Ranges
- To enable the iterative and continuous TEVV of new technological products in real-world conditions, as well as accelerate doctrinal and concept development, as well as interoperability, interested Allies together with relevant NATO Enterprise bodies will pilot in parallel NATO Innovation Ranges. Each Range will be a dedicated standing facility with supporting resources for testing a range of new technologies in different simulated real-world operating conditions. They will provide continuous support for a wide range of testing and de-risking activities, also to ensure interoperability.
B3. NATO Task Force X
- To support Allies in rapidly acquiring, integrating, and deploying new technological products alongside conventional forces to help detect, disrupt, and deter malign activities and threats to meet operational requirements, NATO and Allies will continue to pilot the NATO Task Force X framework. The NATO Task Force X framework provides Allies a rapid technology integration approach for forward- deployed operational units, designed to be applicable and scalable across regions, domains, and problem sets, as required by Allies, allowing establishment of similar initiatives across the Alliance, as necessary.
C. Ensuring that new technological products and services are tailored to Allied defence and security needs
Goals
- Allies endeavour to continue reducing barriers to entry of non-traditional suppliers in appropriate fora by:
- Communicating problem-based demand signals to solicit solutions including from non-traditional suppliers from across the Alliance. To generate viable adoption pathways the demand signals will align with national as well as NATO defence planning and capability development needs.
- In line with national and other relevant norms, promoting inclusive application procedures and avoiding contract terms that favour solely incumbent suppliers.
- Addressing barriers to financing of non-traditional suppliers entering the defence market.
- Taking actions to increase the availability of private capital, which is critical to provide scaling pathways to Allied innovators. Allies will foster financing mechanisms for new technological products and consider strengthening dedicated financing instruments such as the NIF, promoting investments into start-ups and scale-ups in the defence sector.
Enablers
C1. NDPP Demand Signal
- NATO will support Alliance-wide innovation ecosystem engagement by regularly sharing requirements and defence planning priorities with Allied defence innovation entities. This guidance will enable Allied innovation activities to support the implementation of NDPP targets nationally and/or multinationally.
C2. NATO Front Door for Industry
- NATO will establish the NATO Front Door for Industry, enabling NATO and Allies to engage with both defence and non-defence industries through a single interface bringing together all relevant existing tools and mechanisms.
- In support of the NATO Front Door for Industry, DIANA will provide easily accessible public level information to private sector innovators on, inter alia, ongoing innovation challenges, activities and operational experimentation opportunities across the Alliance.
C3. Community of Allied Defence Innovation Entities
- Leveraging the NATO Innovation Network, NATO will establish a community of Allied Defence Innovation Entities with the objective to increase synergies, promote interoperability and leverage collaboration opportunities.
Collaboration with NATO partners
- In order to accelerate the development and adoption of new technologies, Allies have recognised the need to engage with technology-oriented NATO partners that share NATO’s democratic principles and could bring added value to NATO’s work.
