Data Strategy for the Alliance
Background
1. In the 2022 Strategic Concept, Allies affirmed the need to enhance NATO’s technological edge to further strengthen deterrence and defence, and bolster the Alliance’s commitment for collective defence. Moreover, Allies committed to adapt the NATO Command Structure for the information age, leveraging digital technology to ensure military effectiveness. The Digital Policy Committee (DPC) serves as NATO’s lead Council Committee for information management, data management, and data exploitation.
2. The Digital Transformation Implementation Strategy1 (DTIS) provides the framework to enable the Alliance to: conduct multi-domain operations, ensure interoperability across all domains, enhance situational awareness, and facilitate political consultation and data-driven decision-making.
3. With the endorsement of the DTIS, Allies also agreed to establish an Alliance Data Sharing Ecosystem2 (ADSE), a framework that facilitates secure and collaborative access to data resources – including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models – across the Alliance, industry, and academia while ensuring Allies retain control over their data.
4. In light of the above, in February 2025, the North Atlantic Council approved the Data Strategy for the Alliance (DaSA), emphasizing NATO's commitment to leveraging data as an enduring strategic asset, driving sustainable battlespace advantage and business efficiency by 2030. The DaSA sets ambitious targets for 2030 focusing on data curation, governance, and workforce skills, thereby supporting the delivery of an Alliance data centric governance programme:
NATO 2030 Data Target
By 2030, the Alliance Data Sharing Ecosystem, integrated and connected through the NATO Digital Backbone, together with a data-literate workforce and optimized data management processes, facilitate the exploitation of curated, quality data between Allies, the NATO Enterprise, and their respective Communities of Interest.
Aim
5. The Data Strategy for the Alliance aims to accelerate NATO’s transition into a data centric organisation, leveraging quality data for seamless interoperability and integration across all domains by providing guidance for managing NATO data and operationalizing its use for joint and multi-domain operations.
6. Integration with NATO's broader Digital Transformation Strategy ensures alignment with key initiatives, including the establishment of the ADSE and NATO’s Digital Backbone. To support these efforts, users and applications will shift from isolated, private data repositories to shared data spaces and federated data meshes that offer means for the controlled sharing of data products. These sharing environments will be maintained, secured, and optimized to meet mission requirements. This Strategy underscores the requirement for coordinated technology adoption and data management as strategic enablers to connecting the individual components of the data-driven decision-making pyramid (Figure 1).
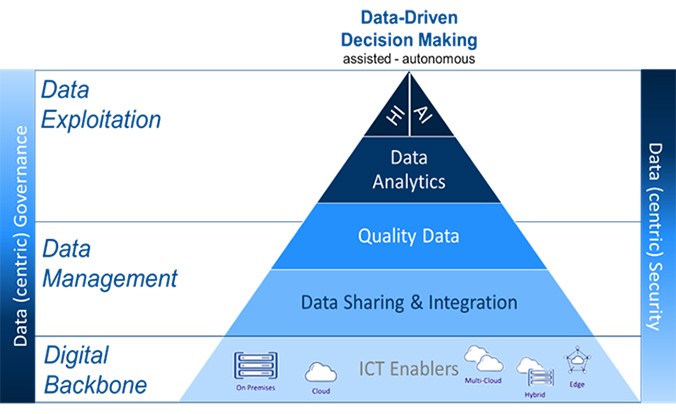
Figure 1: Data-Driven Decision-Making Pyramid
7. Metadata plays a critical role in enabling data sharing. Following the NATO Core Metadata Specification (NCMS), standardized by STANAG 5636, metadata ensures structured and efficient searchability while incorporating best practices from international standards. Data catalogues will further support interoperability by advertising and organizing data assets within communities and across the Alliance through an integrated “catalogue of catalogues.” These federated catalogues will be accessible via web-based interfaces and APIs for both human users and automated systems.
8. In addition, the DaSA establishes a cohesive data governance framework, that aligns initiatives through a unified model, advances the ADSE development, and sets training requirements for military and civilian personnel.
9. In this context, the DaSA focuses on two main areas. First, it consolidates ongoing data-related activities within NATO and identifies gaps in the Alliance’s transition to a data centric approach. Second, it recontextualizes these efforts under a framework of data centric governance and coordinated data management to support the development of a robust data-sharing ecosystem.
Strategic Objectives
10. The Data Strategy serves as a guide for Allies and the NATO Enterprise to align data efforts with the wider interests and objectives of the Alliance, ensuring a coherent approach to improving decision-making and driving operational advantage.
11. To achieve meaningful outcomes from Alliance’s data initiatives, the Strategy outlines the following strategic objectives:
11.1 Data Governance: The Alliance implements clear, coherent, and consistent data governance principles, practices, and controls, ensuring prioritized and automated data management while maintaining data reliability.
11.2 Data Value: Data is produced, distributed, and consumed as a strategic asset, with data assets structured and managed as evolving products that adapt to consumer needs. Ownership and responsibility for data are clearly defined and distributed across cross-functional product teams.
11.3 Data Centric Security: Data shared across the Alliance is protected at source, with Allies and NATO Enterprise controlling all data entrusted in the Alliance based on confidentiality and originator-defined rules to enable NATO’s missions. Adaptive security measures ensure appropriate safeguarding, aligning with operational needs. The Alliance safeguards individuals’ fundamental rights in personal data processing, balancing internationally recognized principles of Personal Data Protection.
11.4 Analytical Maturity: NATO workforce is able to access and create value from relevant data, with leadership fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making. NATO workforce of all literacy levels are provided with the opportunity to make data-informed decisions and apply data principles in daily activity. Scalable data education programs provide role- and team-specific learning pathways for all NATO workforce members.
11.5 Data-Driven Ecosystem: The ADSE enables NATO to share and exploit data at scale. The Alliance fosters a federated environment for collectively sharing, labelling, connecting and exploiting data. Data management focuses on balancing the responsibility to share and the need-to-know, while ensuring discoverability, access, reusability, and compliance with security, legal, and privacy obligations. Strategic data partnerships with industry and academia drive innovation. Allies govern NATO’s data management and sharing, supported by NATO Reference Architectures and standards, which ensure scalable, resilient, secure and interoperable digital services through the NATO Digital Backbone.
Data Principles
12. The successful operationalization of the Data Strategy and the achievement of its strategic objectives rely on key data principles that will govern the design of new data-related capabilities and alignment of existing data initiatives across the Alliance.
12.1 Discoverable: Data is registered, searchable, and its existence visible to authorized individuals or systems, with interoperable metadata.
12.2 Accessible: Data is available for use by authorized individuals, entities and systems through appropriate mechanisms.
12.3 Trusted: Users and systems are able to determine and assess the integrity of data, data-related systems and processes.
12.4 Regulated: NATO data is governed and managed according to international agreements and approved NATO policies and standards.
12.5 Interoperable & Curated: Data, data-related systems and processes ensure interoperability among Allies and the NATO Enterprise.
12.6 Shared: Data is shared to authorized individuals, systems, and organisations using appropriate secure and protected mechanisms, in a manner conducive to collaboration and cooperation.
12.7 Secure: Data is secured and controlled along the whole data life cycle, subject to requirements, legal restrictions, and data owner specifications.
Data Enablers
13. The Alliance will focus engagement on data enablers to ensure that data principles are embedded into resilient and scalable data infrastructure and capabilities.
14. Data enablers are technology-neutral and domain-agnostic principles and standards that specify the basic requirements for Allies, the NATO Enterprise and Communities of Interest to participate in an Alliance data-sharing ecosystem, compliant with agreed rules and directives.
14.1 Governance: Data governance is the framework of policies, procedures, business rules and standards that ensure data is managed as a valuable asset within an organization. Computational data governance lies at the intersection of technology and governance to maintain data quality, security, privacy, and compliance, at scale.
14.2 Architectures: Reference Architectures provide standards, design principles, patterns, and technology recommendations to ensure compliance with agreed strategies and policies. They must be scalable to meet the Alliance's growing data demands and designed to enable efficient data use and interoperability. The Data Centric Reference Architecture for the Alliance (DCRA) embodies a focus on data discoverability, accessibility, quality, and adaptability to evolving technologies. It serves as a key framework for guiding NATO's transition from an application-focused approach to become a data-centric organization.
14.3 Modern Standards for Data Interoperability: Modern NATO standards prioritize accessibility, efficiency, and semantic interoperability, leveraging machine-readable formats and tools for seamless collaboration between humans and technology. The use of NATO’s Domain Ontology for Defence & Security strengthens interoperability and supports the effective use of AI. These advancements enable NATO and industry to adapt swiftly to emerging technologies, digital shifts, and evolving data needs.
14.4 Talent and Culture: NATO will focus on cultivating a workforce that is proficient in data management and utilisation. This enables emphasises the development of a data centric mind-set, ensuring team members are equipped with the skills and knowledge to leverage data effectively in their roles. Fostering a modern, agile workforce is imperative for data talent and culture, comprising civilian and military personnel, and contractors, empowered to utilize data for decision-making, policy creation, and process optimization.
Data Centric Governance
15. The Data Centric Governance Operating Model defines and coordinates data governance practices for Data Strategy implementation within the Alliance and NATO Enterprise. It ensures effective management of data assets, integrates data priorities into strategic initiatives, promotes compliance with data governance principles, and fosters collaboration among data officers across the Alliance to address challenges and oversee policy implementation.
16. Alliance: NATO implements data centric governance through the Digital Policy Committee, which guides and directs the Alliance’s data management efforts and ensures synchronization with other strategic initiatives.
17. The NATO Information Management Authority in Alliance format acts as the Chief Data Officer Council, identifying challenges and overseeing information and data management policy implementation across the Alliance. NIMA in Alliance format serves as the primary venue for collaboration among allied (Chief) Data Officers (CDO), overseeing policy implementation, architectures, and data standards.
18. Nations / NATO Enterprise: Each Ally and the NATO Enterprise are encouraged to establish data centric governance boards at their respective level (e.g. the NIMA in NATO Enterprise format could act as the data centric governance board for the NATO Enterprise).
19. The responsible organisation for Data Strategy implementation within the NATO Enterprise is the Office of the NATO Chief Information Officer (OCIO).
20. The NIMA in Enterprise format, supported by the OCIO, collaborates with NATO data owners to embed controls and establish data capabilities for the NATO Enterprise.
- PO(2023)0191 (INV)
- PO(2024)0316
- Including NATO’s AI Strategy, Federated Mission Networking (FMN), Alliance Persistent Surveillance from Space (APSS), Alliance Future Surveillance and Control (AFSC), Allied software for Cloud and Edge services (ACE), and Digital Ocean.
